An OEM custom brass investment catings provider from China with CNC machining, surface treatment and heat treatment services.
We could provide 3.1 Material Certificate of the casting metal according to EN 10204 if you need. Available inspection methods: dimension testing by CMM, non-destructive testing, chemical composition, mechanical properties, hardness testing, static balancing, dynamic balancing, air pressure and water pressure.
According to the different binder materials used for making the shell, the investment casting could be divided into silica sol casting and water glass casting. The silica sol investment casting process have better Dimensional Casting Tolerances (DCT) and Geometrical Casting Tolerances (GCT) than water glass process. However, even by same casting process, the Tolerance Grade will be different from each cast alloy due to their various castability. Our foundry would like to talk with you if you have special request on the required tolerances. Here in the following are the general tolerances grade we could reach both by silica sol casting and water glass casting processes separately:
✔ DCT Grade by Silica Sol Lost Wax Casting: DCTG4 ~ DCTG6
✔ DCT Grade by Water Glass Lost Wax Casting: DCTG5 ~ DCTG9
✔ GCT Grade by Silica Sol Lost Wax Casting: GCTG3 ~ GCTG5
✔ GCT Grade by Water Glass Lost Wax Casting: GCTG3 ~ GCTG5
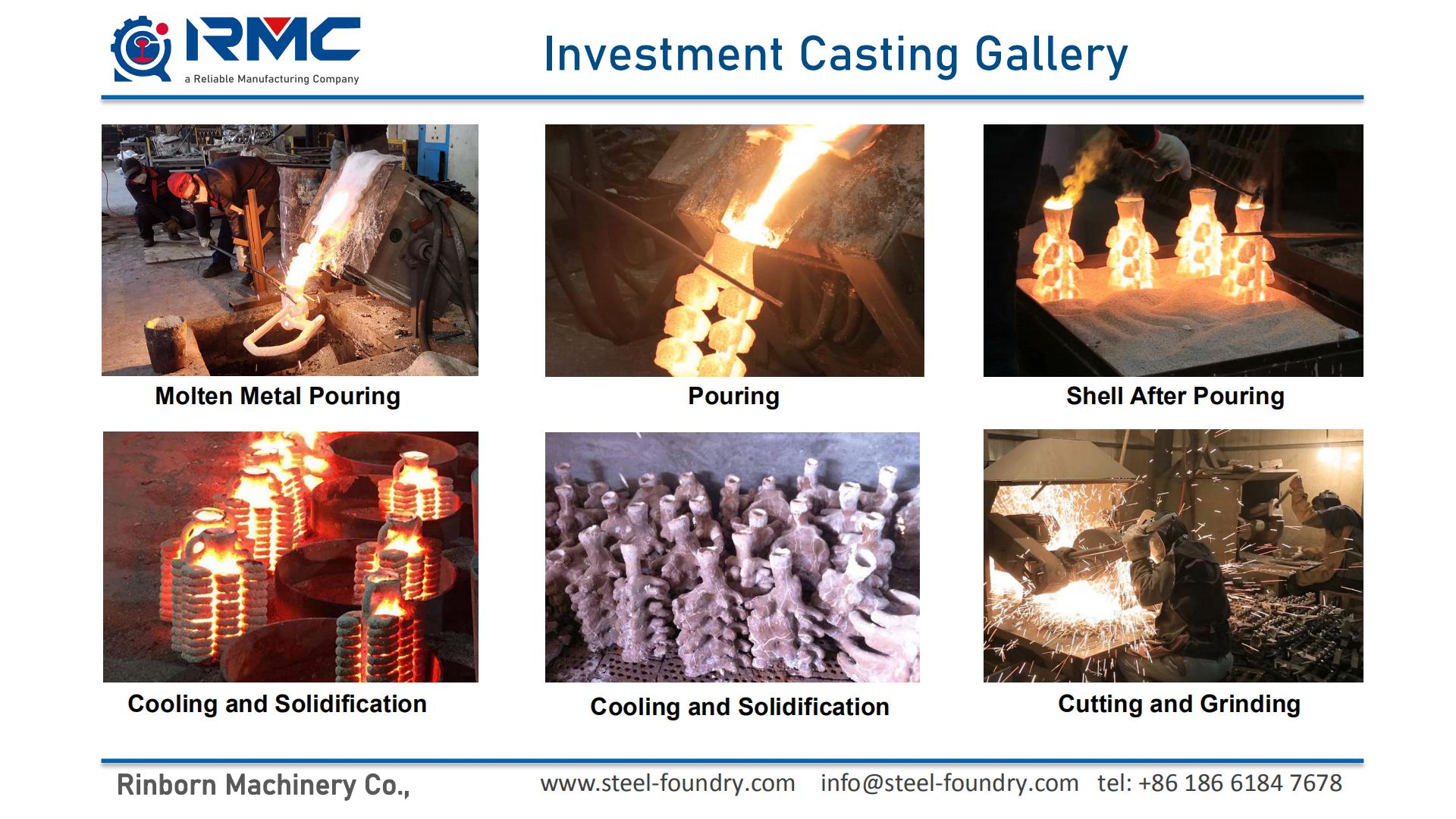
As the copper-based alloys, brass and bronze can be formed into highly complex parts, making them ideal for the investment casting process. Constant cost fluctuations can make these materials very price sensitive, making waste very costly, especially when considering CNC machining and/or forging as a manufacturing process to produce your casting parts. Pure copper is not usually cast. Investment (lost wax) casting is a method of precision casting complex near-net-shape details using replication of wax patterns. Investment casting or lost wax is a metal forming process that typically uses a wax pattern surrounded by a ceramic shell to make a ceramic mold. When the shell dries, the wax is melted away, leaving only the mold. Then the casting component is formed by pouring molten metal into the ceramic mold.
Brass is an alloy composed of copper and zinc. Brass composed of copper and zinc is called ordinary brass. If it is a variety of alloys composed of more than two elements, it is called special brass. Brass is a copper alloy with zinc as the main element. As the zinc content increases, the strength and plasticity of the alloy increase significantly, but the mechanical properties will decrease significantly after exceeding 47%, so the zinc content of brass is less than 47%. In addition to zinc, cast brass often contains alloying elements such as silicon, manganese, aluminum, and lead.
Casting brass has higher mechanical properties than bronze, but the price is lower than bronze. Cast brass is often used for general purpose bearing bushes, bushings, gears and other wear-resistant parts and valves and other corrosion-resistant parts. Brass has strong wear resistance. Brass is often used to make valves, water pipes, connecting pipes for internal and external air conditioners, and radiators.
| Materials for Investment Casting Process at RMC Foundry | |||
| Category | China Grade | US Grade | Germany Grade |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | 1Cr17, 022Cr12, 10Cr17, | 430, 431, 446, CA-15, CA6N, CA6NM | 1.4000, 1.4005, 1.4008, 1.4016, GX22CrNi17, GX4CrNi13-4 |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | 1Cr13, 2Cr13, 3Cr13, 4Cr13, | 410, 420, 430, 440B, 440C | 1.4021, 1.4027, 1.4028, 1.4057, 1.4059, 1.4104, 1.4112, 1.4116, 1.4120, 1.4122, 1.4125 |
| Austenitic stainless steel | 06Cr19Ni10, 022Cr19Ni10, 06Cr25Ni20, 022Cr17Ni12Mo2, 03Cr18Ni16Mo5 |
302, 303, 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 329, CF3, CF3M, CF8, CF8M, CN7M, CN3MN | 1.3960, 1.4301, 1.4305, 1.4306, 1.4308, 1.4313, 1.4321, 1.4401, 1.4403, 1.4404, 1.4405, 1.4406, 1.4408, 1.4409, 1.4435, 1.4436, 1.4539, 1.4550, 1.4552, 1.4581, 1.4582, 1.4584, |
| Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel | 05Cr15Ni5Cu4Nb, 05Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb | 630, 634, 17-4PH, 15-5PH, CB7Cu-1 | 1.4542 |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | 022Cr22Ni5Mo3N, 022Cr25Ni6Mo2N | A 890 1C, A 890 1A, A 890 3A, A 890 4A, A 890 5A, A 995 1B, A 995 4A, A 995 5A, 2205, 2507 |
1.4460, 1.4462, 1.4468, 1.4469, 1.4517, 1.4770 |
| High Mn Steel | ZGMn13-1, ZGMn13-3, ZGMn13-5 | B2, B3, B4 | 1.3802, 1.3966, 1.3301, 1.3302 |
| Tool Steel | Cr12 | A5, H12, S5 | 1.2344, 1.3343, 1.4528, GXCrMo17, X210Cr13, GX162CrMoV12 |
| Heat Resistant Steel | 20Cr25Ni20, 16Cr23Ni13, 45Cr14Ni14W2Mo |
309, 310, CK20, CH20, HK30 | 1.4826, 1.4828, 1.4855, 1.4865 |
| Nickle-base Alloy | HASTELLY-C, HASTELLY-X, SUPPER22H, CW-2M, CW-6M, CW-12MW, CX-2MW, HX(66Ni-17Cr), MRE-2, NA-22H, NW-22, M30C, M-35-1, INCOLOY600, INCOLOY625 |
2.4815, 2.4879, 2.4680 | |
| Aluminum Alloy |
ZL101, ZL102, ZL104 | ASTM A356, ASTM A413, ASTM A360 | G-AlSi7Mg, G-Al12 |
| Copper Alloy | H96, H85, H65, HPb63-3, HPb59-1, QSn6.5-0.1, QSn7-0.2 |
C21000, C23000, C27000, C34500, C37710, C86500, C87600, C87400, C87800, C52100, C51100 | CuZn5, CuZn15, CuZn35, CuZn36Pb3, CuZn40Pb2, CuSn10P1, CuSn5ZnPb, CuSn5Zn5Pb5 |
| Cobalt-base Alloy | UMC50, 670, Grade 31 | 2.4778 | |
| INVESTMENT CASTING TOLERANCES | |||
| Inches | Millimeters | ||
| Dimension | Tolerance | Dimension | Tolerance |
| Up to 0.500 | ±.004" | Up to 12.0 | ± 0.10mm |
| 0.500 to 1.000” | ±.006" | 12.0 to 25.0 | ± 0.15mm |
| 1.000 to 1.500” | ±.008" | 25.0 to 37.0 | ± 0.20mm |
| 1.500 to 2.000” | ±.010" | 37.0 to 50.0 | ± 0.25mm |
| 2.000 to 2.500” | ±.012" | 50.0 to 62.0 | ± 0.30mm |
| 2.500 to 3.500” | ±.014" | 62.0 to 87.0 | ± 0.35mm |
| 3.500 to 5.000” | ±.017" | 87.0 to 125.0 | ± 0.40mm |
| 5.000 to 7.500” | ±.020" | 125.0 to190.0 | ± 0.50mm |
| 7.500 to 10.000” | ±.022" | 190.0 to 250.0 | ± 0.57mm |
| 10.000 to 12.500” | ±.025" | 250.0 to 312.0 | ± 0.60mm |
| 12.500 to 15.000 | ±.028" | 312.0 to 375.0 | ± 0.70mm |