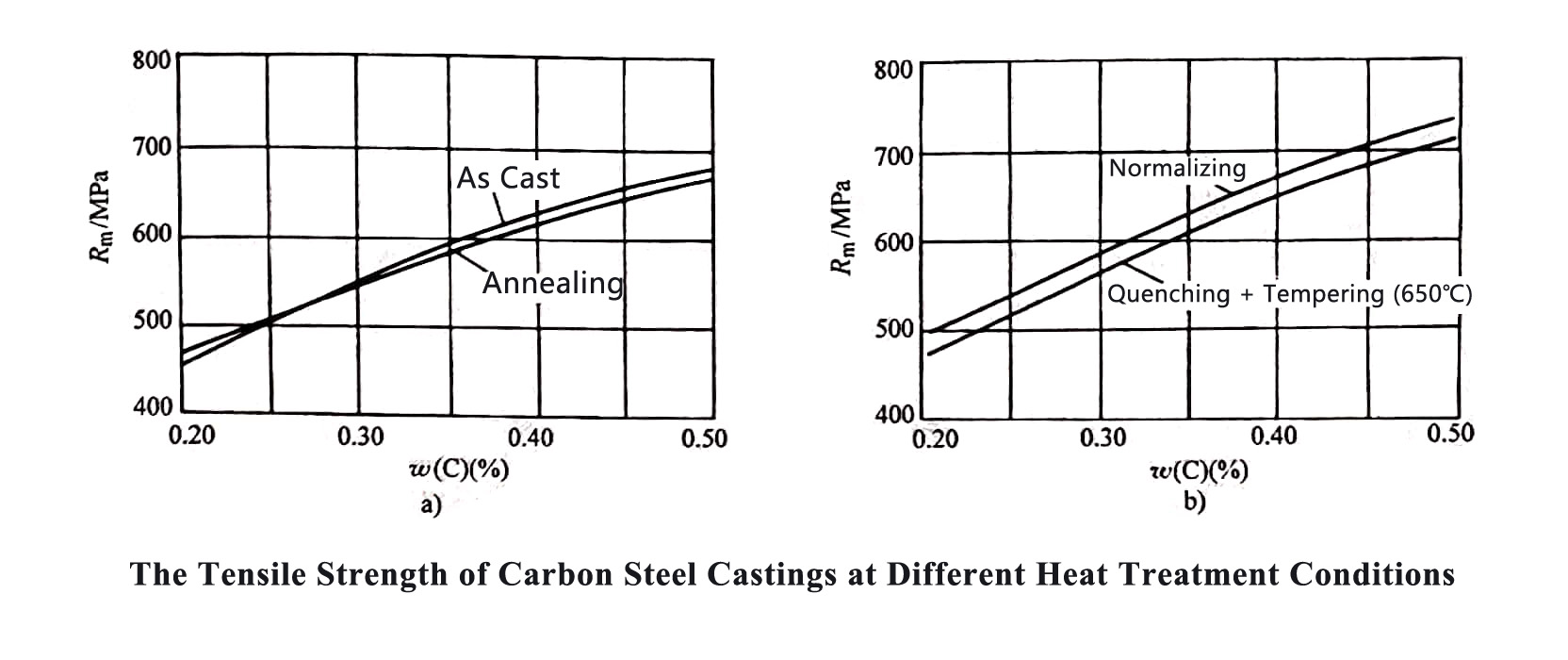
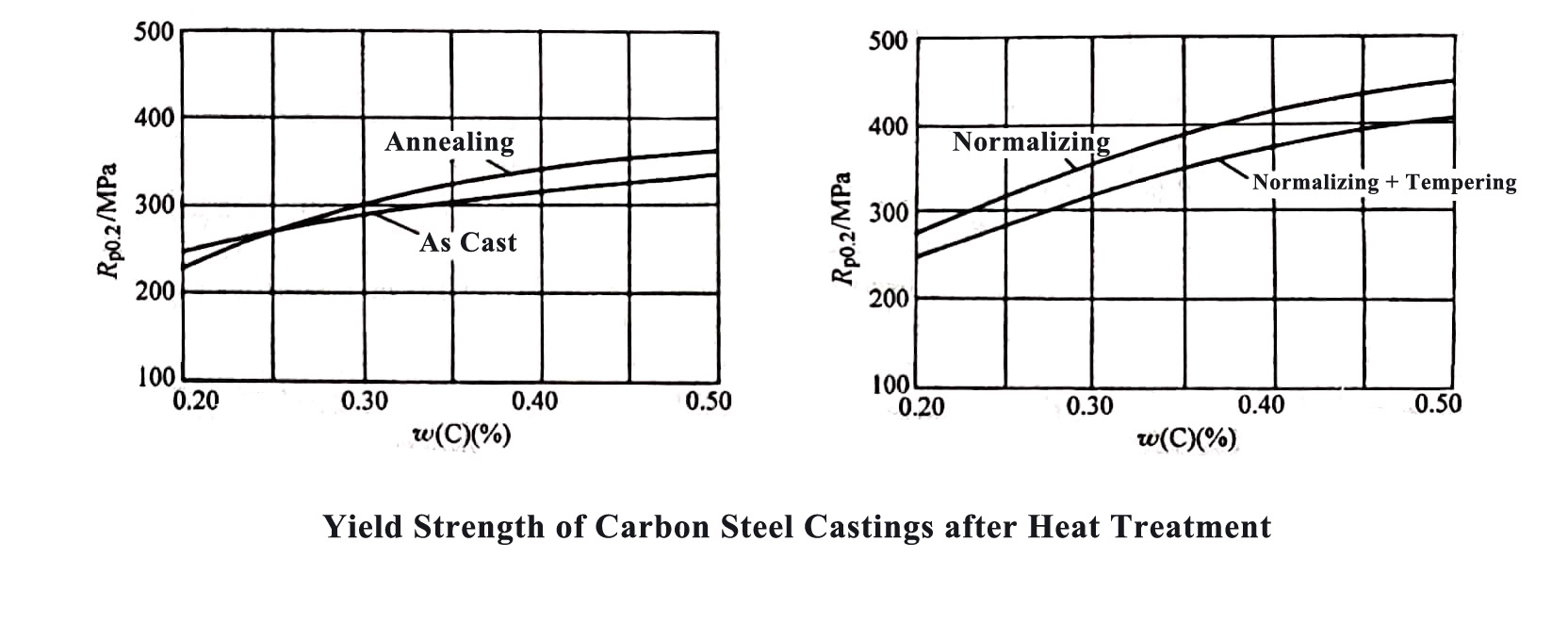
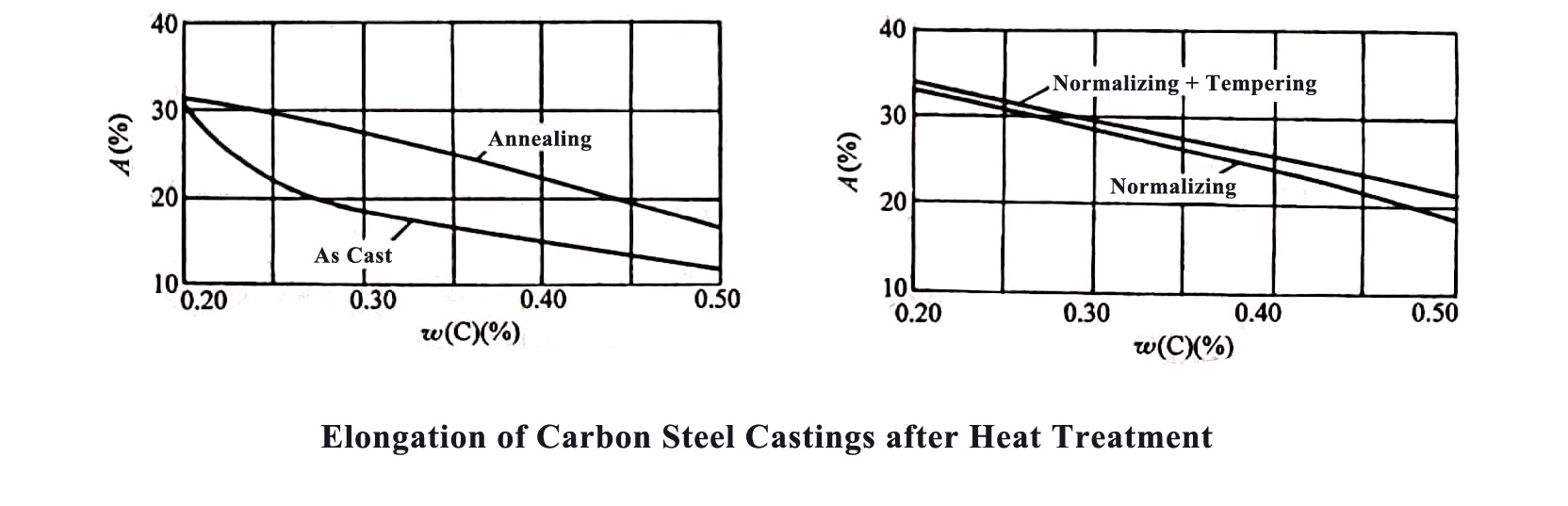
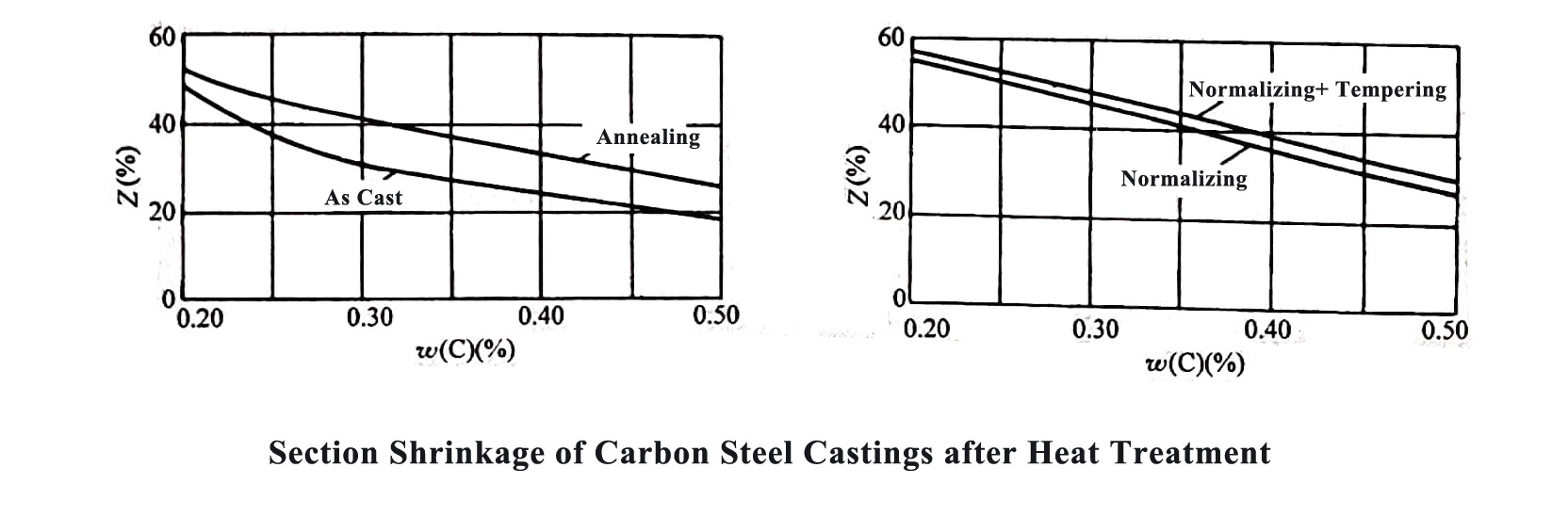
The heat treatment methods usually used for carbon steel castings are: annealing, normalizing or normalizing + tempering. The influence of these three heat treatment methods on the mechanical properties of cast carbon steel is shown in the figure below.
| The Annealing Temperature and Hardness of Carbon Steel Castings | ||||||
| Grade of Carbon Steel | Carbon Content / % | Annealing Temperature / ℃ | Holding Time | Cooling Method | Hardness / HBW | |
| Wall Thickness / mm | Time / h | |||||
| ZG200 - 400 | 0.10 - 0.20 | 910 - 880 | < 30 | 1 | Cooling to 620℃ in the furnaces and then cooling in the air | 115 - 143 |
| ZG230 - 450 | 0.20 - 0.30 | 900 - 870 | 133 - 156 | |||
| ZG270 - 500 | 0.30 - 0.40 | 890 - 860 | 143 - 187 | |||
| ZG310 - 570 | 0.40 - 0.50 | 870 - 840 | 30 - 100 | increase 1 hour / 30 mm | 156 - 127 | |
| ZG340 - 640 | 0.50 - 0.60 | 860 - 830 | 187 - 230 | |||
The mechanical properties of normalized cast steel are slightly higher than those of annealed cast steel. As the degree of undercooling during the transformation of the structure is relatively large, the hardness will be higher, and its cutting performance is also better.
| The Normalizing and Hardness of Carbon Steel Castings | |||||
| Grade of Carbon Steel | Carbon Content (%) | Normalizing Temperature / ℃ | Tempering | Hardness / HBW | |
| Temperature / ℃ | Cooling Method | ||||
| ZG200 - 400 | 0.10 - 0.20 | 930 - 890 | 540 - 610 | in furnace or air | 126 - 149 |
| ZG230 - 450 | 0.20 - 0.30 | 930 - 890 | 540 - 610 | in furnace or air | 139 - 169 |
| ZG270 - 500 | 0.30 - 0.40 | 890 - 860 | 550 - 620 | in furnace or air | 149 - 187 |
| ZG310 - 570 | 0.40 - 0.50 | 890 - 850 | 550 - 650 | in furnace or air | 163 - 217 |
| ZG340 - 640 | 0.50 - 0.60 | 870 - 830 | 550 - 650 | in furnace or air | 187 - 228 |
For carbon steel castings with high carbon content and complex shapes, in order to eliminate residual stress and improve toughness, tempering treatment can be carried out after normalizing. The tempering temperature is generally 550℃-650℃, and then cool in air.
When the carbon content is higher than 0.35%, the cast carbon steel parts can also be quenched and tempered (quenched + high temperature tempered). Small carbon steel castings can be directly quenched and tempered in the as-cast state; large or complex-shaped carbon steel castings should be quenched and tempered after normalizing.
| The Quenching and Tempering Temperature and Hardness of Carbon Steel Castings | |||
| Carbon Content % | Quenching Temperature / ℃ | Tempering Temperature / ℃ | Hardness After Tempering / HBW |
| 0.35 - 0.45 (Small Batch) | 850 - 830 (Cooling in Water) | 300 - 400 | 364 - 444 |
| 400 - 450 | 321 - 415 | ||
| 510 - 550 | 241 - 286 | ||
| 540 - 580 | 228 - 269 | ||
| 580 - 640 | 192 - 228 | ||
| 0.45 - 0.55 (Small Batch) | 830 - 810 (Cooling in Water or Oil) | 550 - 630 | 220 - 240 |
| 450 | ≈ 269 | ||
| 550 | ≈ 248 | ||
| 650 | ≈ 228 | ||
| 0.30 - 0.40 (Mass Batch) | 840 -880 (Cooling in Water or Oil) | 520 - 550 | 229 - 269 |
| 530 - 560 | 217 - 255 | ||
| 540 - 570 | 207 - 241 | ||
| 550 - 580 | 187 - 229 | ||
| 0.40 - 0.50 (Mass Batch) | 820 - 840 (Cooling in Water or Oil) | 530 - 560 | 229 - 269 |
| 550 - 580 | 217 - 255 | ||
| 560 - 590 | 207 - 241 | ||
| 570 - 600 | 187 - 229 | ||
Post time: Jul-23-2021